
Atoms, elements and compounds - the fundamental basics to GCSE chemistry
First step: get your periodic table out. Have a little look at it. Do not worry, you will not have to remember it all!
What is an element?
A substance containing particles called protons, neutrons and electrons, which forms the make up of an atom. Each element is made of one type of atom. Thus, no two atoms share an element (or box in the periodic table.)
The periodic table categorises elements using groups and periods, which tell us some of the structural and chemical properties each element will have. For example, calcium is an element in group 2 and period 3. But we’ll go into more detail about that later…
All substances are made from roughly 100 elements, as listed in the table. Rather than writing each and every atom, symbols can be used. For example, the atom oxygen has the symbol ‘O’ and calcium has the symbol ‘Ca.’
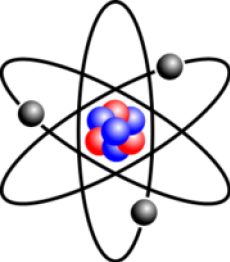
How is an atom arranged?
In the centre we have the nucleus. This is composed of particles called protons and neutrons. Surrounding the nucleus are the orbiting electrons which are arranged in what we call shells. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge and electrons have a negative charge. For GCSE level, that’s as complicated as it gets, but if you decide to go onto A level you will learn about electron orbitals. Atoms can react with other atoms to join and form a compound. When the compound is formed, different types of bonds are formed depending on what two elements have reacted.
As protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge, and the number of protons in an atom are equal to the number of electrons, this means that overall the atom has no charge. However, this is not the case for ions. This will make more sense later on. The number of protons is called the atomic number, this number will be displayed as the bottom number of the element in the periodic table. The number above is called the mass number. The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons. An easy way to remember this is the ‘mass number’ is the ‘massive number,’ in other words the bigger number. Thus, we can work out the number of neutrons in an atom by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. Additionally, we can work out the electronic number through it being the same as the proton number, and therefore the atomic number.
So, let’s put this into practice to make sure you understand.
Question: Find bromine on the periodic table. How many protons, neutrons and electrons does chlorine have in it? What group and period is bromine in?
Answer:
Bromine is in group 7 and period 4.
The mass number is 80. The atomic number is 35.
Number of protons = 35
Number of neutrons= 45
Number of electrons = 35
A summary:
All substances are made of atoms
An element contains one type of atom
An atom is made up of a number of protons, neutrons and electrons
Image:https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atom

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.