
GCSE BIOLOGY REVISION: REPRODUCTION
Please note: Text in bold is what the AQA GCSE biology specification requires an understanding of.
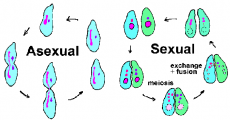
Students should understand that meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed.
What is meiosis?
A type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores.
What is mitosis?
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth.
Mitosis division results in two identical daughter cells whilst meiosis results in 4 non-identical sex cells.
There are some similarities between the two types of division, but it is very important to know the differences. Do not get them mixed up!
Sexual reproduction involves the joining (fusion) of male and female gametes:
sperm and egg cells in animals
pollen and egg cells in flowering plants.
Terminology
Gametes- are a mature haploid male or female germ cell which is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction.
Germ cell- a cell containing half the number of chromosomes of a somatic cell and able to unite with one from the opposite sex to form a new individual; a gamete.
Fertilisation- a process in sexual reproduction that involves the union of male (sperm) and female (ovum) gametes (each with a single, haploid set of chromosomes) to produce a diploid zygote.
Haploid- having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
Diploid- containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
Sexual reproduction requires two parents. The nuclei of male and female gametes fuse together to form a zygote (fertilisation.) Each gamete is haploid. In order to create a human embryo, gametes must join to get a full set of chromosomes.
The gametes in:
Animals are sperm (male) and eggs (female)
Flowering plants are pollen (male) and eggs (female)
In sexual reproduction, there is mixing of genetic information which leads
to variety in the offspring. The formation of gametes involves meiosis.
As there is genetic mixing, this means that offspring produced by sexual reproduction are genetically different to the parents and each other (variation).
Features of sexual reproduction using meiosis
Making genetic information copies
The cell divides twice to form four gametes (each has a single set of chromosomes)
Each gamete is different
In humans, the two number of chromosomes the body requires is 46. 23 chromosomes= haploid.
______________ ________________ ___________________
(23 chromosomes) + (23 chromosomes ) = ( 46 chromosomes )
______________ ________________ ___________________
sperm cell egg cell diploid zygote
A zygote will mature into an embryo. The number of cells increase by mitosis. As the embryo develops, cells will begin to differentiate/ specialise.
Differentiate- make or become different in the process of growth or development
Specialise- become adapted to a special function in a particular environment.
Image- http://igbiologyy.blogspot.com/2014/04/148-summary-of-reproduction.html

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.