
GCSE BIOLOGY REVISION: ORGANISATION OF AN ECOSYSTEM
LEVELS OF ORGANISATION
Please note: Text in bold is what the AQA GCSE biology specification requires an understanding of.
Students should understand that photosynthetic organisms are the producers of biomass for life on Earth.
Producer à consumer
You may be asked a question where you need to fill in a food pyramid, in which case, producers go at the bottom, they are in the most abundance and so have the biggest area on the triangle. You may be asked to point out which is the producer, producers are plants (organisms that can photosynthesise.) What is biomass? The mass of living material.
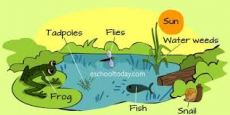
Feeding relationships within a community can be represented by food chains. All food chains begin with a producer which synthesises molecules. This is usually a green plant or alga which makes glucose by photosynthesis.
Feeding relationships identify what organisms eat what and what organisms are eaten by others. This is shown through levels of organisation in an ecosystem.
An example food chain:
Grassà rabbits à fox
If arrows are not given, you should still know what organism eats what based on being able to identify the producer. All animals above the producer are consumers. The first is a primary consumer, then secondary then tertiary consumers. Don’t worry, examiners will not expect you to know complex food chains with obscure animals, they will be very simple and easily understood. Predators are animals that hunt and kill other animals. They are at the top of the food chain in a predator-prey relationship. Prey are animals that are eaten by predators.
Decomposers are bacteria and fungi that break down dead and decaying organisms in a process called decomposition, also known as rotting. They do so by releasing enzymes onto dead matter which breaks it down and then later consuming it. They are vital recyclers necessary to our environment. Broken down parts can be used as nutrients for plants additionally.
A range of experimental methods using transects and quadrats are used by ecologists to determine the distribution and abundance of species in an ecosystem.
You may have done a practical in school to investigate these techniques. Questions regarding this point in the specification are limited as there is only so much that they can ask. Thus, it will be useful for you to try out all past paper questions regarding this topic! It is likely they will repeat the type of question. Candidates can often be caught out through making silly errors. For example, a quadrat may show half an insect. But insects are not found in halves, you have to round it to the next whole number!
If you missed out on doing this experiment, do not worry. Here is a good video example to help with your understanding.
https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/z9nwtv4/revision/4
image-https://eschooltoday.com/ecosystems/what-is-an-ecosystem.html

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.