
GCSE BIOLOGY REVISION: INFECTION AND RESPONSE
Please note: Text in bold is what the AQA GCSE biology specification requires an understanding of.
Monoclonal antibodies (for candidates doing higher tier only)
Students should be able to describe how monoclonal antibodies are produced.
Monoclonal antibodies are produced from a single clone of cells. The antibodies are specific to one binding site on one protein antigen and so are able to target a specific chemical or specific cells in the body.
They are produced by stimulating mouse lymphocytes to make a particular antibody. The lymphocytes are combined with a particular kind of tumour cell to make a cell called a hybridoma cell. The hybridoma cell can both divide and make the antibody. Single hybridoma cells are cloned to produce many identical cells that all produce the same antibody. A large amount of the antibody can be collected and purified.
Mono = one
Clone = identical copy
Therefore, monoclonal antibodies are identical copies of one antibody.
What are antibodies?
Lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, produce types of proteins called antibodies. They are complementary to specific antigens (protein structures) found on the surface of pathogens. The production of antibodies are used for the attack of foreign antigens recognised by lymphocytes.
The formation of monoclonal antibodies:
Firstly, inject the antigen into a mouse
Naturally the mouse will produce lymphocytes that produce antibodies specific to the antigen
Spleen cells produce lymphocytes. The spleen cells are removed during a small operation
Fusion of spleen cells with human cancerous white blood cells called myeloma cells. This forms hybridoma cells, these cells divide indefinitely
The hybridoma cells divide and produce millions of monoclonal antibodies specific to the original antigen
Uses of monoclonal antibodies
Pregnancy test kits
Cancer diagnosis and treatment
Other diagnostic uses
Pregnancy test kits
These kits use monoclonal antibodies that are designed to bind with a hormone called HCG. HCG is found in the urine of pregnant women. Monoclonal antibodies are found attached to pregnancy test sticks which the women shall urinate on. If pregnant, the HCG in her urine will bind to the monoclonal antibodies on the test stick. This binding causes a colour change or pattern change indication pregnancy. This binding is highly specific.
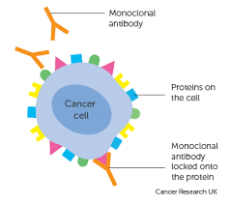
Cancer diagnosis and treatment
Cancerous cells have antigens. Specific monoclonal antibodies can be designed to bind with these antigens. These antibodies are injected and the monoclonal antibodies will bind to cancer cells and cause them to clump together. This makes cancerous tumours easier to spot. Once identified, the tumour can be treated or removed.
They also can treat cancer by:
Carrying drugs that have been attached to them, to the tumour
They can encourage the immune system to attack the cancer cells directly
Other diagnostic uses
Monoclonal antibodies can be used to diagnose infections like HIV and AIDS, as well as herpes and chlamydia. Some are also attached to dyes that go fluorescent under UV light. This makes them detectable and can therefore identify disease
image -https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/cancer-in-general/treatment/targeted-cancer-drugs/types/monoclonal-antibodies

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.