
GCSE BIOLOGY REVISION: HOW MATERIALS ARE CYCLED
Please note: Text in bold is what the AQA GCSE biology specification requires an understanding of.
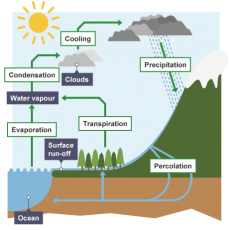
The water cycle provides fresh water for plants and animals on land before draining into the seas. Water is continuously evaporated and precipitated.
Processes – evaporation, condensation, transport, precipitation, surface runoff, infiltration, transpiration.
What happens in each stage
Evaporation is where the water turns into a gas. It therefore changes state going from liquid to gas. How does this happen? Well the energy from the sun evaporates the water molecules. This water comes from the sea, puddles, ponds and lakes.
Condensation is where a gas converts to a liquid, this occurs after evaporation. The water cools itself and forms clouds.
Transport is where water within the clouds can be blown many miles by strong winds, thus clouds are transported to other areas. Fun fact, this is why tropical reasons experience lots of clouds and heavy rainfall.
Precipitation is where rain, snow, hail and sleet fall from the sky.
Surface runoff is where most of the water is absorbed into the ground after precipitation has occurred. If large amounts of water fall then some of the water will run along the surface of the ground.
Infiltration is where water that has fallen as precipitation is absorbed into the ground. This can be stored within underground rocks called aquifers.
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers.
The carbon cycle returns carbon from organisms to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide to be used by plants in photosynthesis.
Carbon is also an essential element for life on earth. Our cells in our bodies are made up of carbon (and other elements.) Carbon is constantly cycled through the atmosphere; this process is highly important. Carbon enters the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide from combustion and respiration. Producers absorb carbon dioxide to synthesise carbohydrates, for example, plants do this in the photosynthesis reaction. Animals feed on the plant passing the carbon compounds along the food chain. The majority of carbon consumed is exhaled as carbon dioxide formed during respiration. Eventually the animals and plants will die. Dead organisms are eaten by decomposers, these decomposers return the carbon from the dead bodies into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. Some conditions block decomposition. In these cases, the plant and animal material may be used for fossil fuels that can be used for combustion. Some carbon is locked and stored away in sea beds. Volcanic activity releases carbon into the atmosphere.
Questions regarding the carbon cycle are normally straight forward. It is important that you are able to explain the cycle. A good way to test whether you understand it is to explain it in diagrammatic format using as few words as possible. Carbon cycle questions can be big mark questions so it is worth knowing it well!
If you plan to take A level biology, luckily for you it does not get much more complicated than this. So, try to remember what you have already learnt.
Here is a useful and exciting video to help with your understanding of the carbon cycle:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aLuSi_6Ol8M
image- https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/topics/zxfd3k7

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.