
GCSE BIOLOGY REVISION: CELL DIFFERENTIATION
Please note: Text in colour is what the AQA GCSE biology specification requires an understanding of.
Students should be able to explain the importance of cell differentiation.
What is cell differentiation?
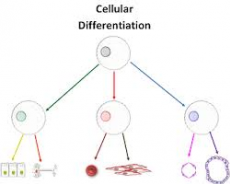
The process by which a cell that is less specialised develops into a more specialised cell type, the cell differentiates. This means the cell will start to develop organelles required for correct functioning.
Animal and plant cells begin by sexual reproduction (meiosis.) They begin life as a single cell (fertilised egg or zygote.) The cell then divides to produce multicellular organisms. After division, there are multiple cells which can be used for various cells.
Let’s put this into simpler terms:
Picture this, you have one simple cell, it divides, it divides again, and again, until there are now 100 cells. Some cells can develop into red blood cells, some into liver cells, some into brain cells, they will all start to look different because different cells have different requirements in order to perform the correct function.
As an organism develops, cells differentiate to form different types of cells.
• Most types of animal cell differentiate at an early stage.
For this specification, you do not need to explain why this is, you just need to be able to recognise this fact and know that animal cells differ to plant cells. They will not question you as to why this is.
• Many types of plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughout life.
The same point given for animal cells applies to this bullet point. Cells of the meristem can differentiate any time during the plants life into all types of cells.
A comparative table to summarise key points:
Key feature
Animals
Plants
Differentiation occurrence
Most differentiation occurs at early stages of life
Throughout life
Where cell division happens
In most tissues
Majority of division occurs at meristems found in tips of shoots and roots
How growth happens
Increasing number of cells
Cell enlargement mainly
In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacement. As a cell differentiates it acquires different sub-cellular structures to enable it to carry out a certain function. It has become a specialised cell.
Where are adult stem cells found in animals?
Brain
Eyes
Muscle
Bone marrow
Skin
Heart
Blood
Liver
Where are adult stem cells found in plants?
Meristems (found in tips of shoots and roots)
So, when cells get damaged, stem cells can be used in order to replace damaged cells, or they can be used as repair tools.
When a cell has its acquired organelles, it can complete its function, it is specialised.
image- https://study.com/academy/lesson/applications-of-cell-differentiation-benefits-risks.html

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.