
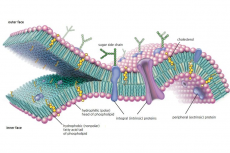
A premature stop codon mutation prevents full translation of mRNA producing truncated CFTR. Truncated CFTR is not functional and will not undergo trafficking therefore the protein will be absent at the membrane. Splicing defect mutations result in CFTR mRNA that is not properly processed. Some functional CFTR may be produced and present in the plasma membrane, but far less than that of a non-cystic fibrosis sufferer. Deletion mutations (like
F508) result in defected post translational folding and trafficking and thus a reduced amount present on the cell surface. Gating defects occur when a mutation does not affect the presence of CFTR on the cell surface but its ability to open and closed is inhibited or the channel is narrowed. CFTR can also regulate other membrane proteins, if defected this has implications of other faulty proteins such as further ion channels, leading to further imbalance of electrolytes.
How is cystic fibrosis treated?
There is no cure for cystic fibrosis however can be treated to relieve the symptoms caused by the faulty gene. Antibiotics may be prescribed to get rid of lung infection, mucus-thinning medications can be taken and bronchodilators relax muscles around airways to the lung to allow increased airflow. However, the membrane still remains faulty, and so treatment is needed throughout the entirety of the patient’s life.
What is Muscular Dystrophy?
Muscular dystrophy is a muscular disease that causes the weakening and breakdown of skeletal muscles over a period of time. It is an inherited disorder that has different stages of severity. Dystrophin protein is found in the membrane of muscle fibre (sarcolemma) and works as a shock absorber.
What is the cause of Muscular Dystrophy?
A mutation of the dystrophin gene -a results in the absence of the protein, damaging the plasma membrane. Dystrophy holds responsibility for connecting muscle fibre cytoskeletons, in its absence, too much calcium is able to penetrate through the cell membrane. Calcium concentration changes the volume of water entering the mitochondria, leading to the cell bursting. Dystrophin has the responsibility of binding actin and actin is necessary for the osmotic response. The increased permeability of the membrane allows soluble enzymes to leak out of the cell and ions to diffuse into the cell. It is vital for electrolyte balance to be regulated and for enzymes to be kept within their appropriate compartments, a more fragile membrane (caused by muscle dystrophy) prevents this from happening.
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s is a neurodegenerative disease which occurs in the later stages of many people’s lives. It is formed by changes in the membrane phospholipid composition. Neural membranes have the responsibility of insulating cell contents from the surrounding exterior environment and allow the transport of nutrients, ions and other compounds. In the membrane is a molecule called amyloid- β precursor protein and has the role of helping the neurone grow and repair. Normally the protein is used, broken down and recycled by the enzyme -secretase and -secretase. If -secretase and -secretase break down the protein then the product is not soluble creating a monomer called amyloid beta which are sticky and join together to form plaques around the neurone. The plaques hold the ability to interact with the membrane and interfere with synapses, impairing the normal functioning of the brain. Inside the cell membrane, tangles can form. Tau (a protein in the membrane) stops microtubules from breaking apart allowing them to function. Beta amyloid plaque outside the neurone initiate pathways inside neurone that leads to the activation of kinase, an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups, to tau. This causes tau to change shape, so no longer has the correct tertiary structure. Tau then leaves the microtubules and clumps together and gets tangled. The microtubules cannot signal effectively which sometimes leads to apoptosis of the neurone.
Altogether, proteins in the plasma membrane are highly crucial in the cells ability to operate correctly. Minor changes in genetic coding can have large effects on the cell, sometimes to the extent of cell death.
Image Credits
https://fthmb.tqn.com/TpBy42Nvk0Vhbk2ogL607hwwCTw=/768x0/filters:no_upscale()/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.