

Carbohydrates. A word you have probably heard your entire life but do you actually understand what the word means? They are essential biological molecules and, believe it or not, they contain carbon! Most carbohydrates are polymers.
What are polymers?
A polymer is a substance which has a molecular structure built up chiefly or completely from a large number of similar units bonded together. In simpler terms, similar small molecules are joined together to form a big molecule. These small molecules are called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are the monomers that make up polysaccharides.
Glucose for example is a monosaccharide. It can join together to form the polysaccharide starch. Glucose is a hexose monosaccharide (meaning it contains 6 carbon atoms and is in a hexagonal shape) and it can come in two forms; alpha glucose and beta glucose. They do look very similar so it is important to recognise what makes them different. In alpha glucose, on the first carbon, there will be a hydrogen attached to it above the ring and a hydroxyl (OH) group attached below the ring. In beta glucose it is the reverse (hydroxyl group above the ring and hydrogen below the ring.) That is the only difference, the rest of the structure is exactly the same. The different glucoses will be able to bond to different molecules to form different polysaccharides. Two alpha glucose molecules join to form maltose (a disaccharide). Other dissacharides are sucrose (formed from alpha glucose and fructose) and lactose (formed from beta glucose and galactose.) Lots of alpha glucose molecules can join to form the polysaccharide amylose.
So how do monosaccharides form disaccharides, and then polysaccharides?
They do so using a condensation reaction. A condensation reaction involves removing a hydrogen from one monomer, and a hydroxyl group from the second monomer, this produces water and as a result a glycosidic bond forms. Thus a condensation reaction is removing water to form a bond which connects the two monomers together (synthesis.) This reaction is reversible, a disaccharide can be broken back into two monomers through a hydrolysis reaction. A hydrolysis reaction is where water is added to split the monomers. To synthesise a polysaccharide it is the same process happening continuously.
Ribose is another example of a monosaccharide. This time, it has a five carbon sugar thus it is a pentose monosaccharide and is shaped pentagonally. All carbohydrates have the same three chemical elements; carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
Carbohydrates are a good energy source and their shapes are useful to their functions. For example glucoses shape makes it good for energy storage and makes it soluble. Its solubility is useful as glucose is needed all over the body for respiration. Therefore as it is needed all over, it needs to be transported in the blood. As it is soluble, it can easily be transported in the blood to wherever it is needed. The glycosidic bonds contain energy, so when broken the energy can be used for reactions, the breakdown of ATP (the universal energy currency) into ADP and inorganic phosphate.
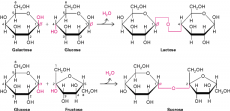
Image credits:
https://www.biology-questions-and-answers.com/images/Carbohydrate-Properties.jpg
https://ibhumanbiochemistry.wikispaces.com/file/view/ch2f10.gif/31798121/ch2f10.gif

0 Comment:
Be the first one to comment on this article.